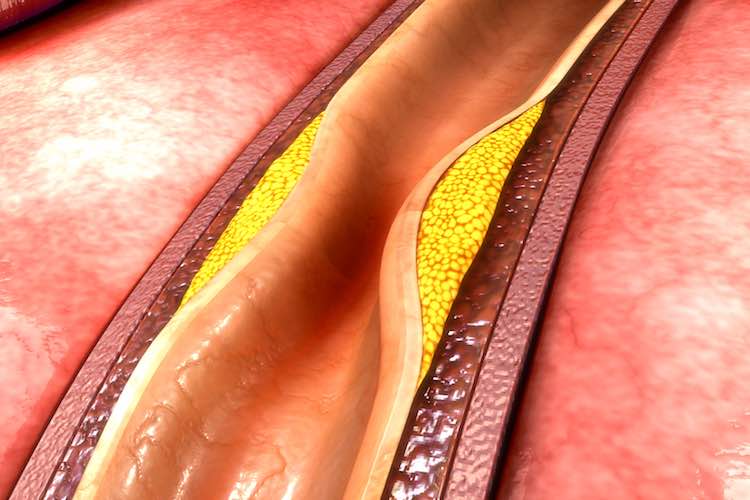
The aim of coronary artery bypass surgery is to bypass blocked coronary arteries and improve blood flow to the heart muscle. This can relieve angina and help prevent heart attacks.
stroke
Video: Exercise trumps genetic risk of heart disease
Keeping fit can reduce your risk of heart disease, even when your genetic risk profile is high.
Heartbeat
The heartbeat is usually a regular rhythm, but when disturbed it becomes irregular and is felt as palpitations. Find out about extra beats and arrhythmias and when to visit the doctor.
Video: Blood clots – reducing the risk
Every year 30,000 Australians develop blood clots in their legs or lungs and 5000 of them will die. Many blood clots happen during or after a hospital stay and new hospital standards are aimed at reducing this risk.
Pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism (PE) happens when a blood clot blocks one of the arteries in the lungs. Find out about the causes, diagnosis, treatment and prevention of PE.
Heart attack
A heart attack (myocardial infarction) means the blood supply to part of the heart muscle has become blocked. Early treatment can reduce muscle damage.
Heart transplants
There are treatments for heart failure, but for some people a transplant is the best option. Heart transplantation is generally a successful procedure for advanced heart disease.
von Willebrand disease
Find out about Von Willebrand disease, an inherited bleeding disorder that affects up to one in 100 people.
Blood and bleeding
Blood makes up about 8 per cent of a person's body weight. In a normal-sized adult, there are about 5 litres of it. Blood is not a single substance, but a suspension of several components, held together in a straw-coloured fluid called plasma.
Heart failure overview
Heart failure is when your heart can’t effectively pump blood around your body, but it doesn’t mean your heart is about to stop or fail completely – you can live with heart failure for many years.