Food poisoning: causes, symptoms and tips on how to prevent it.
digestive
Barrett’s oesophagus
Barrett's oesophagus affects some people with gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Having Barrett's oesophagus increases your risk of developing oesophageal cancer.
Irritable bowel syndrome: what you need to know
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a disorder in which the normal rhythmic movement of your gut (bowel) is disturbed – this can lead to abdominal pain, bloating and excessive gas.
Gilbert syndrome
Gilbert syndrome is a mild condition in which there is an excess of bilirubin in the blood. You may at times develop mild jaundice, with slight yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes.
Hepatitis C infection
People infected with hepatitis C virus can develop chronic (ongoing) infection. Treatment with antivirals can cure hepatitis C and prevent the complications of chronic infection.
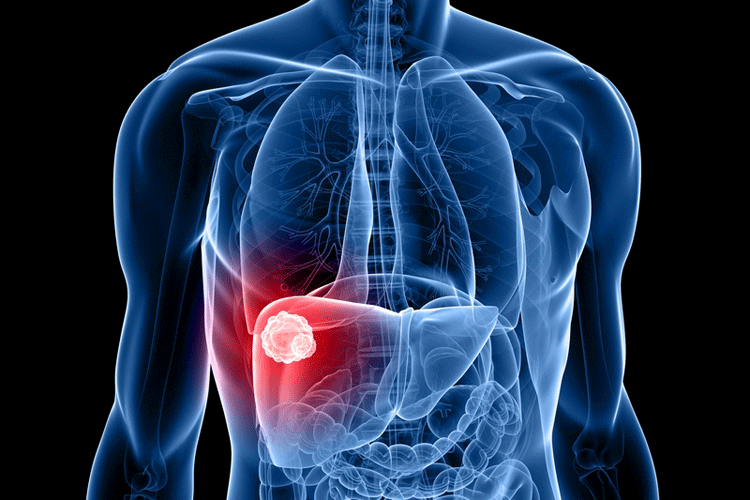
Liver cancer
Liver cancer can start within the liver (called primary liver cancer) or come from other parts of the body and spread to the liver (called secondary liver cancer, or liver metastases).
How your food is digested
The digestive system is a series of hollow organs such as the stomach and small intestine. Digestion starts in the mouth with the production of enzymes.
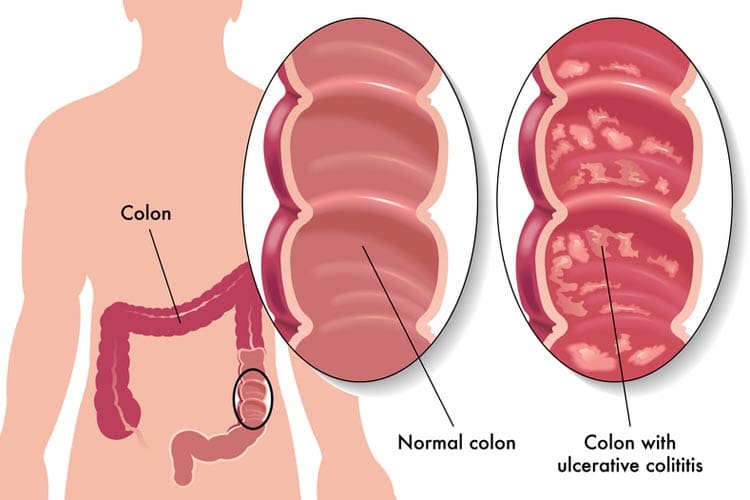
Ulcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis is one of 2 major types of inflammatory bowel disease — a condition which causes the bowel (colon) to become inflamed. It affects people of all ages, but usually starts between 15 and 30 years.
Heartburn treatments
Treatment for heartburn will depend on how often your heartburn occurs and how much it impacts on your life. Treatments include antacids, medicines or surgery, as well as self-help measures.
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is when you have frequent or severe reflux symptoms, such as regular heartburn. If you have complications of reflux, you are also considered to have GORD.