Up to half a million Australians have type 2 diabetes and don't know it. In most people, it starts silently, but it's important to be aware of early warning signs. Diabetes Week is about early detection, so if you have any symptoms, see your doctor.
sugar
A diet for diabetes prevention
A diet high in carbohydrate and fibre and low in fat helps weight loss in people at high risk of type 2 diabetes.
Diabetes and Indigenous Australians
Indigenous Australians are at higher risk of type 2 diabetes than non-Indigenous Australians.
Diabetes complications
Diabetes complications include both long-term and emergency complications. Find out more about these health problems and reducing the risk of complications.
Diabetes and taking medications for other conditions
Some medicines can affect blood sugar levels and alter blood glucose control in people with diabetes. And some medicines can worsen complications.
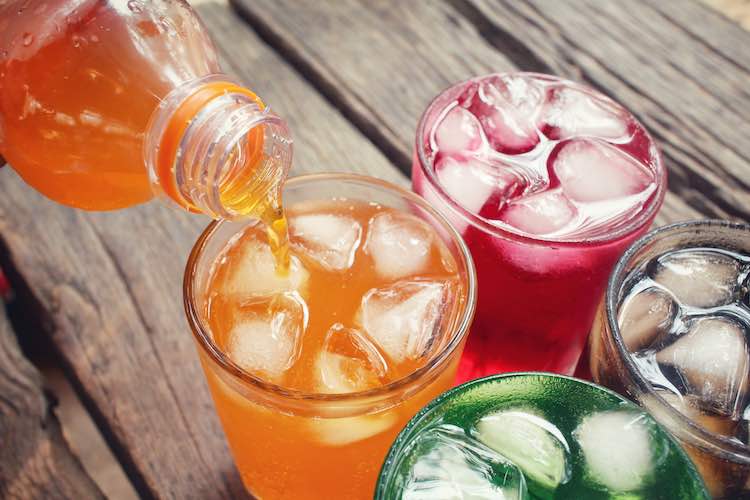
Sweetening the risk of type 2 diabetes
Consumption of sugar-sweetened beverages is associated with increased incidence of type-2 diabetes.
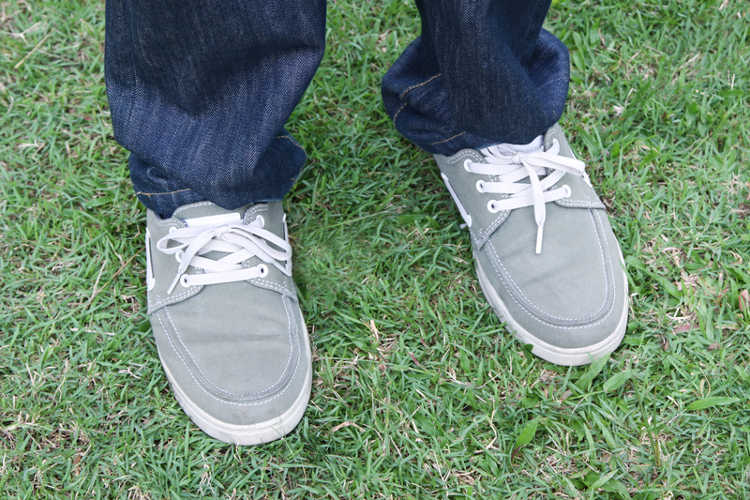
Diabetes can affect your feet
When you have diabetes you need to take very good care of your feet to prevent serious complications. Diabetes can damage the nerves and the blood supply in your feet.
Hypoglycaemia in diabetes
Hypoglycaemia is a condition in which there is an abnormally low level of glucose in the blood. It's important to be aware of the symptoms and how to treat a 'hypo'.
Ketoacidosis: a complication of diabetes
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious condition that can occur as a complication of diabetes. People with DKA have high levels of glucose and ketones in the blood, making it more acidic than usual.
Insulin: how it works
Insulin is a hormone that helps control blood sugar levels. Made by the pancreas, insulin stimulates the uptake of glucose from the bloodstream into cells, lowering your blood sugar level.