- General Information
- See Your Pharmacist or Medical Professional
- Treatment Tips
- Treatment Options
- More Information
General Information
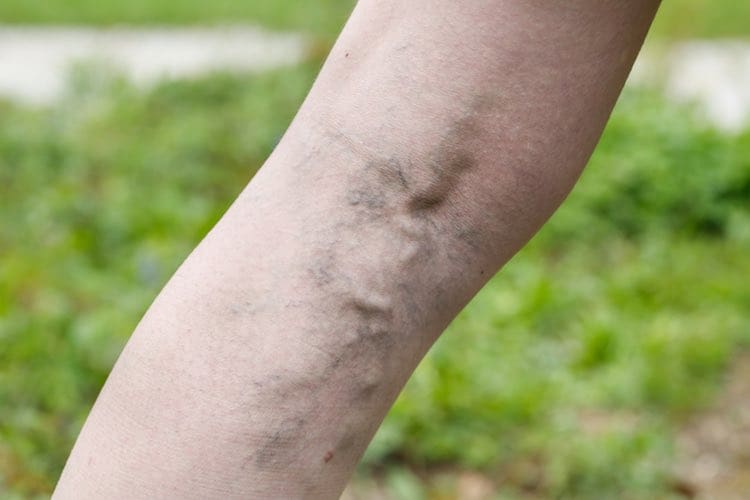
Varicose veins
Varicose veins are enlarged, prominent veins usually found on the legs. Varicose veins can look twisted or bulging, and are usually blue or dark purple. Many people with varicose veins will not have any other symptoms, but sometimes they can be painful and can cause aching, throbbing or itching. These symptoms tend to be worse if you have been on your feet for a long time.
Varicose veins develop when blood pools in the veins, causing them to enlarge. The reasons some people develop varicose veins are not fully understood, but some risk factors have been identified.
Varicose veins do not always need to be treated, but people who experience pain or discomfort or develop complications, such as leg ulcers, may require treatment. Others may wish to have treatment for cosmetic reasons.
Risk factors for varicose veins
- being female
- increasing age
- pregnancy
- family history of varicose veins
- being overweight
- having a job which involves standing for long periods
Deep vein thrombosis and air travel
Blood clots are formed when your blood stops moving and coagulates. If a clot, or thrombus, forms in the deep veins of the legs, this is called deep vein thrombosis (DVT). If all or part of this clot is dislodged, it can travel through your blood circulation and cause a blockage in the narrower blood vessels of your heart or lungs.
Air travel of more than 4 hours increases the risk of DVT. This is thought to be due to many factors, such as reduced cabin pressure in the aircraft at high altitudes, reduced movement in cramped conditions and dehydration. This causes fluid to move from your blood vessels into the surrounding tissue, causing thickening of the blood and making clots more likely to form. In addition, the blood in your legs moves less.
Normal movement of the calf muscles when walking helps to pump blood from the legs to the heart, but this doesn’t happen when you sit still for long periods, making clots more likely to form.
Research suggests that air travel can increase your risk of DVT two- to three-fold. However, it is important to realise it is not just long-distance air travel or flying economy class that puts people at risk of DVT. Sitting in one position for too long is a major factor and this can also occur during long bus, car or train journeys.
Risk factors for DVT
- being over 40 years of age
- being overweight
- heart failure
- pregnancy or having recently given birth
- cancer
- varicose veins
- taking medications containing oestrogen, such as the oral contraceptive pill or hormone replacement therapy (HRT)
- chronic health conditions such as heart disease and blood disorders
- recent major surgery or trauma, particularly involving the lower limbs
- previous history of DVT
- family history of DVT
- smoking
- long-distance flights
See Your Pharmacist or Medical Professional
- if your varicose veins are causing pain or discomfort
- if the skin on your legs is discoloured, swollen, broken or weeping
- if your varicose veins are getting worse despite self-management
- if you are concerned about the appearance of your varicose veins
- if you are planning a long-distance flight and you think you may be at risk of developing DVT
Treatment Tips
Prevention of varicose veins
- maintain a healthy weight
- exercise regularly
- give up smoking
- avoid standing or sitting still for long periods
- avoid high-heeled shoes and tight-fitting clothes around or below the waist
- rest for short periods with your legs elevated above the level of your heart
- if you have varicose veins, discuss wearing support stockings with your pharmacist or doctor
Prevention of DVT
- drink plenty of water
- go easy on alcohol and caffeine during the flight
- do ankle and knee exercises while seated at least every half hour
- wriggle toes frequently
- walk down the aisles regularly, or if travelling by car, stop frequently and take a walk
- consider wearing support stockings; ask your pharmacist for advice
- take only short naps unless you are in a sleeping position
- seek medical advice prior to flying if you have any of the above risk factors
Treatment Options
- aspirin is not recommended to prevent DVT from occurring during air travel
Support stockings
e.g. Jobst range, Juzo, Mediven range, RxFit, Scholl Flight Socks, Sigvaris, Therafirm, Varisan, Venosan
- support stockings, also known as graduated compression hosiery, help blood to flow from the lower legs back towards the heart
- support stockings are tightest at the ankle and become gradually less tight as they go up the leg; this helps to move blood gently up your legs and prevents it from pooling
- compression hosiery is classified into three different grades: class 1 (light), class 2 (moderate) and class 3 (extra firm):
- class 1 compression is recommended for people with tired aching legs, mild varicose veins, mild ankle swelling, and to prevent ankles and feet swelling during long flights, e.g. Scholl Flight Socks
- class 2 compression is used for people with moderate to severe varicose veins, pronounced ankle swelling after vein surgery, and to prevent recurrence of venous leg ulcers
- class 3 compression is used for people with severe varicose veins or ankle swelling, active leg ulcers and to prevent leg ulcers recurring
- your pharmacist can measure you to ensure the correct fit
- measurements for support stockings are best taken as early as possible in the morning
- after washing do not dry support stockings in a clothes dryer; refer to manufacturer’s information for laundry details
- wear rubber gloves when putting on support stockings to prevent fingernails and jewellery snagging the stockings
- trim rough nails on hands and feet to avoid snagging the stockings
- TED stockings are prescribed by doctors and used in the hospital setting. They should not be used to treat or prevent varicose veins or as travel socks
More Information
Availability of medicines
- GENERAL SALE available through pharmacies and possibly other retail outlets.
- PHARMACY ONLY available for sale through pharmacies only.
- PHARMACIST ONLY may only be sold by a pharmacist.